Bhim Nath Baral
Associate Professor
Department of Political Science
Prithvi Narayan Campus
Tribhuvan University, Pokhra, Nepal
 Text begins from the previous issue:
Text begins from the previous issue:
Democratization of diplomacy- By the turn of twentieth century, diplomacy is subjected to democratic control. The participation of the people in the politics of a state and the importance of public opinion led to the democratization of diplomacy where the governments were no longer the domain of aristocrats. The diplomacy is being developed as the sole affair of minister and diplomats.
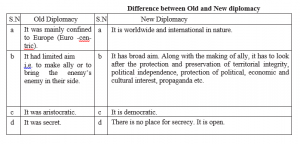
# Changing issues- Old diplomacy had limited agendas. Its main purpose was to facilitate in the relation among the rulers or bring the enemy’s enemies at their side. But new diplomacy contains several issues like economics, social, environmental, world peace and so on.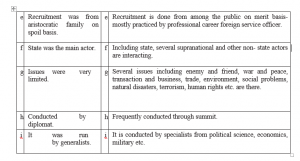
#The cultural Diplomacy: The diplomacy which aims to obtain its goal through the conduction of cultural programme is termed as cultural diplomacy. It is the diplomacy which is based on cultural strength. Each nation tries to establish its cultural supremacy and the basis of establishing mutual relationship becomes culture. It was much used in the past. The concept of cultural diplomacy was coined by former Soviet Union. The diplomacy after Stalin (1953) was adopted to bring the uncommitted or the developing world in their favor (Roy, 1978:371). This diplomacy is more related to ‘Trade’ and ‘Aid’ policy of the then Soviet Unio which tried to influence the people of other countries and search for new allies in the world. So, Soviet Russia introduced the policy of development of economic and cultural relations with all countries. This policy became very useful to extend the relation with the countries in the East.
The policy of cultural diplomacy aimed to influence the people of newly independent countries of the world. Motivating the people of third world towards communist philosophy was the primary goal of the diplomacy. Effort was also made to draw the attention of the people of the world towards Soviet culture, social and economic life through economic, technical and educational aid. They have also exchanged their cultural diplomats. The then Soviet government strengthened its relation through this diplomacy. Generally, the devices like establishment of cultural society, exchange of films, translation programme, press and cultural relation, group flattery policy etc. were used to increase their influence.
By using those devices, Soviet government presented its originality in the field of diplomacy. It was found very effective to attract the third world countries towards communist system. The group flattery policy “workers of the world be united” became the original theory of Communism. They sent their scientists, trainers, actors etc. in the developing countries and cultural relation was consolidated.
The relevancy of this sort of diplomacy still exists in present day politics. In each nation, big or small, rich or poor, has its own culture and civilization. Some weak nations can have superior culture as compared to those of powerful nations. In order to spread culture print media is used and cultural conferences are held in which cheap and free of cost materials about country’s cultural heritage and civilization is distributed. Cultural delegates are exchanged and efforts are made to maintain an environment of goodwill and mutual understanding.
These days, cultural delegates are becoming a part of diplomacy. Nepal’s diplomatic dealings is much more affected by its cultural aspects too. Bhrikuti, Araniko, Manjushree etc. can be regarded as the cultural dignitaries in course of Nepal-China relation whereas Sita, Ram, Janak and several other cultural dignitaries and other heritages of Nepal and India have their impact in diplomatic dealings. The powerful countries still have their cultural centers in small and developing nations.
# Western and Eastern Diplomacy:
Diplomacy is further divided into two more types i.e. Western and Eastern. Historically, the Asian and Western nations have shared a common problem, appropriate cultural responses to changing international environment that have resulted in distinct diplomatic style. The diplomatic intercourse in ancient Asia, which is commonly known as ‘Bharatvarsha’ was mainly based on Hindu mythology. The famous diplomats like Kautilya, Shukra and their writings along with the provisions made in holy books like Ramayana, Mahabharat have provided guidelines in diplomatic dealings. Side by side, the western civilization and the concerned writers have their own contribution in diplomacy as mentioned in introductory topics.
But the concept of Western and Eastern Diplomacy became the subject of hot discussion during post Second World War period. This period made clear cut division of world on the basis of political ideology which gave birth to cold war. The world war allies dramatically divided into two hostile blocs i.e. Capitalistic West headed by USA and Communist East headed by the then Soviet Union. This incident divided the world into West and East.
After the establishment of UNO, peace treaty was signed. Relations, however, deteriorated by a process of action and reaction publicly manifested by Churchill’s Fulton speech in the spring of 1947 in which he referred to the ‘Iron Curtain’. The Soviet takeover of European satellites, the Truman doctrine, and the formation of NATO, the communization of China, the Korean War and the initiation of atomic rivalry maintained a condition of cold war. The trend of forming several military organizations added more tension in world politics.
Generally, the diplomacy adopted by USA and her democratic allies is termed as Western Diplomacy. The USA emerged as one of the most powerful countries after World War II. She gave up her policy of isolation and began to actively participate in world politics. She became the custodian of democracy and had to clearly define the basic principles of diplomacy and policy. Simply, the western diplomacy has the following characteristics:
# It believes that capitalist system is the best in the world.
# It is anti-communist.
# Diplomacy should be morally sound.
# Diplomacy should be conducted on the basis of democracy, human right and the preservation of other human values.
# It is open.
# It believes in economic liberalism.
# Aid contributes a lot in diplomacy.
# Western type of democracy is the ideal form of government and every possible effort should be made to save it.
The Eastern Diplomacy, on the other hand, is mainly based on the policy adopted by Soviet Union and Communist world as well. When the Communists came in power in Soviet Union in 1917, they published all the secret treaties concluded by former rulers. Basically, after the beginning of cold war, Soviet Union developed herself as the counter gravity of world power. Warsaw Pact had formed and COMECON (Council for Mutual Economic Assistance) was introduced to unite the communist countries. As a counterpart of Marshall Plan, Molotov plan was introduced for the reconstruction of communist countries. It became the fundamental objective of their diplomacy to spread communism in the world. Its diplomacy remained very effective during cold war period. But after the disintegration of Soviet Union in early 1990s, Russia and other few communist nations have continued this diplomacy. Generally, it has the following characteristics:
# It is the foremost duty of diplomacy to spread communism.
# Western democracy should be replaced by people’s democracy where the former is not a real democracy.
# Diplomacy believes that the country had neither permanent friends nor permanent enemies.
# It is anti-capitalist.
# It believes in extensive propaganda.
# World communist movement may be threatened by capitalists. So, communists should be prepared to save it from possible encroachment.
# It believes in aid diplomacy.
# Goodwill visit can play effective role in diplomacy.
# Collective security system can best serve in the protection of communism.

Types of Diplomacy: Bilateral and Multilateral Diplomacy:
According to Nicolson, ”the growing sense of the community of nations and increasing appreciation of the importance of public opinion and rapid increase in communication have clearly enlarged the diplomat’s functions and enhance their importance. The result has been the ”worldwide intermeshing” of the foreign officers and diplomatic posts through which most of the formal contracts between states are now maintained (Quoted, Palmer and Perkins, 2015:93). As the number of international organizations, groupings, and conferences increased, multilateral diplomacy took on added significance. It is said that conference diplomacy was a precursor of institutional diplomacy and parliamentary diplomacy is a byproduct of institutional diplomacy. All these forms of diplomacy are inter-connected and inter- related and come under multilateral diplomacy (Malhotra, 2014:339). Their separate discussion is made below.
Conference Diplomacy:
A large part of international dealings is conducted through the medium of international conferences and the periodic meetings of regional and international organizations. This is known as conference diplomacy (Malhotra, 2014:339). The term ‘diplomacy by conference’ is used to describe the frequent resource to multilateral method by which nations are doing business with each other. So, it is taken as the multilateral method of diplomatic negotiation in which leaders or representatives of more than two countries participate and characterized by numerous and complicated rules of procedure. It is a technique of diplomatic negotiations. ‘Conference diplomacy’, “according to Mallik, ‘is the procedure where by the special delegation headed usually by special chief delegates, assemble to settle special problems and questions of wide international interest’ (Quoted, Roy, 1978:138). So, it can be taken as the collective way of conducting negotiation for the purpose of solving international problems. In other words, conference diplomacy is that forum where not only the diplomats or representatives tackle with the international problem commonly but also heads of state or heads of government of different nations including the organizational representatives get together and discuss upon the world problems with their solutions.
Conference diplomacy is not the concept of recent origin. This notion came into practice since the time of immemorial when the states realized the need for the settlement of conflicts. The Greek city states settled their disputes by various methods and one such method was that of arranging conferences and meeting. But this method could not remain in practice during medieval period. Its systematic execution commenced alone with the establishment of League of Nations after the First World War. However, its root goes at least in the Congress of Westphalia (1642-1648) which laid foundations for the modern state system. ‘Diplomacy by conference’ was gradually coming into vogue from the beginning of the twentieth century. The Hague conference of 1899 and 1907 can be regarded as some early examples of Conference Diplomacy (Roy, 1984:108). Some writers are of the opinion that the Congress of Vienna (1815) and Aix- La- Chapelle (1818) can be taken as the first and historical example of conference diplomacy (Roy, 1978:139). Besides these, the Panama Conference of American State (1826),st Petersburg Conference (1864), Congress of Paris (1856) and Congress of Berlin (1884-1885) were also the examples of conference diplomacy. Though many important international problems were discussed and solved in those conferences, these were convened for special purposes and could not be considered as regular feature of diplomatic devices of the period (Roy, 1984:108).
However, it was the post-world war period, the practice of conference diplomacy started to play a very important role in international relations. A number of conferences followed in succession e.g. Paris Peace Conference (1918), the Disarmament Conference at Washington (1922), the Locarno Conference (1925), the Disarmament Conference at Geneva (1927), the London Conference (1930), the Sanfrancisco Conference (1945) are some notable examples of conference diplomacy during and after world wars. Since World War-II, conference diplomacy became a routine feature of international relations relating to the emerging issues like disarmament, environment, trade, sustainable development, human right, and refugee and so on. According to Palmer and Perkins, six thousand to ten thousand sessions of international conferences are now held each year (2015:100). Some deal with highly technical subject and are attended by relatively few persons, mostly experts in their field. Others are general international meetings, attended by hundreds of persons including many foreign ministers or diplomats of the highest rank.
The early twentieth century made the practice of conference diplomacy more popular. Basically, there were many matters of pressing importance which required quick decision among the parties of the war but this was not possible by the ordinary methods of diplomatic communication (Roy, 1984:108). It was felt that the problems must be solved as quickly as possible if the dangers and destruction of the magnitude of war were to be avoided. It was also realized that the problems of colonial and imperialistic power could best be solved by understanding each other’s view point at the conference table. With the passes of time, international conferences started rapid course in tackling with world problems. Now a days, the United Nations seems to be the main place for conference diplomacy. Likewise, the commonwealth nations have their own tradition of conference and the other small conferences have been held to discuss important political and diplomatic problems.
The conference diplomacy is divided into different three categories. Diplomacy by independent conference falls under its first category where the countries beyond particular organization take part in conference. It is the second category conference where the organizations like NATO, OAS, and OAU take part in conference. It is also known as coalition diplomacy and often create problems. Finally, parliamentary diplomacy comes under its third category where most numerous of all are the conferences held under the aegis of the United Nations and its agencies. According to D.N. Mallik, “conference diplomacy can further be divided into three on the basis of the technicality of issue and involvement of the personnel in the conference. They are: diplomacy by technical conference, diplomacy by ministerial conference and summit diplomacy” (Quoted, Roy, 1978:147-148).
Merits of conference diplomacy: No doubt, conference diplomacy is gaining popularity at modern times. Such diplomacy is considered as the strong weapon to control war. Generally, it has the following merits:
This practice is very helpful to take instant decision over the issue which is useful in solving the dispute in time.
Generally, prime ministers, president, foreign ministers or the similar responsible dignitaries of the state are the participant who are responsible for the execution of the decision taken in the conference.
It develops a sense of trust by understanding each other’s view point. Real intimacy and friendship contribute materially to the success of diplomacy by conference, by rendering possible absolute frankness in discussion.
There is high chance of flexibility which assists in ending the disputes.
It is possible to make pacific settlement of international disputes and avoid war.
The face to face contract of the representatives of various countries helps to avert deadlocks by giving priority to collective interest instead of promoting national interest exclusively.
The embassies and diplomatic missions are not in a position to negotiate or to take bold decision during negotiation. They have to pass several steps in taking decision which may be costly and lengthy too. But at the conference, the decisions are instantly taken and thus time and resource are saved.
This method is gaining popularity mainly because of its democratic nature. Hence, all big or small, rich or poor, developed or developing, get opportunity to express their view as decisions are normally taken on majority basis. It gives small states a voice and in equal vote with great powers.
Conference diplomacy is open in nature. It formally discards the secrecy.
It is the conference diplomacy which is found very useful in the promotion of international cooperation and development of the spirit of brotherhood. Using common forum for the solution of problem automatically makes them responsible for common good. Frequent meeting at the conferences develops personal contracts and thus spirit of brotherhood develops among them. Realization of each other’s problems promote international understanding which is also helpful to avoid war.

Weaknesses of diplomacy by conference:
In spite of wide range of acceptability, conference diplomacy is not free from criticism. Generally, its weaknesses are found as below.
There is high chance of misunderstanding among the delegates because of the views expressed by a particular participant.
Such method ignores public opinion.
Some issues require secrecy but there is no possibility of maintaining secrecy.
Conference diplomacy is also criticized as the means of propaganda and picnic spot.
It is costly as well as straining for the host country to arrange such conferences.
There is no possibility of secret negotiation in conference diplomacy as secret negotiation sometimes becomes very essential for concluding an open treaty. But under the system of conference diplomacy, there is no provision of secret negotiations, which is one of its serious weaknesses.
# Shortly to begin with “Types of Diplomacy: ED. Upadhyaya.
